
Prehistory: the birth of cheese
~ 3 million years BC – 2000 BC
Milk
- 9000 BC: sheep and goat farms
- 8000 BC: cattle farms in Asia
- 5000 BC: cattle farms in Europe
- 2000 BC: first dairy in Shumen

Science and Technology
- Mastery of fire
- Cooking of food
- First draining of curds
- First tools
- Invention of the wheel in Mesopotamia
Antiquity: butter and cheese
~ 2000 BC – AD 476
Milk
- Butter in Asia
- Cheese: eaten by Roman soldiers
- 1400 B.C.: first cheeses in Mesopotamia and India
- 100 B.C.: first pressed cheeses

Science and Technology
- Rise of mathematics and medicine in Greece (Aristotle, Euclid, Thales, Hippocrates, et al.)
- Sundial
- Money, paper and corrective glasses in China
- Gaul barrels for storing liquids
- Roman balance
Middle Ages: the rise of cheese
~ 476 – 1492
Milk
- Crucial role of monasteries in cheesemaking and maturing: Maroilles, Munster, Beaufort, etc.
- Emergence of other cheeses: Comté, Gruyere, Saint-Nectaire, etc.
- 1267: first cooperatives in France
- Use of rennet to preserve cheese

Science and Technology
- Decimal numeral system including zero in India
- Invention of Arabic numerals
- Compass and astrolabe
- Wood-block printing in China and Gutenberg printing press
Renaissance: major discoveries
~ 1492 – 1680
Milk
- First hygiene regulation for milk sold in towns
- Fermented milk in Turkey and Central Europe
- Rise of butter: hand-crank butter churn
- 1500: appearance of Reblochon
- Creation of whipped cream by François Vatel for Louis XIV
- Exchange of cheesemaking skills and techniques in Europe
Science and Technology
- Birth of modern surgery (Ambroise Paré)
- 1543: sun-centred solar system (Copernicus)
- Probability theory: Pascal, Hugens and Fermat
- 1609: observation of the sun rotating on its axis (Galileo)
- 1671: law of gravity (Newton)
- Thermometer (Galileo)
- 1665: microscope observation of plant cell tissue (Hooke)
- New plants introduced to Europe by explorers
The Age of Enlightenment: intellectuals
~1680 to 1850
Milk
- Creation of Mont d’Or Vacherin cheese
- 1791: invention of Camembert (Marie Harel)
- First animal health measures
- Livestock improvement by crossbreeding
- First veterinarian schools
- Founding of agronomic science
- 1840: Petit Suisse
Science and Technology
- 1735: classification of plants and animals (Linné)
- 1789: birth of modern chemistry (Lavoisier)
- 1780: isolation of lactic acid (Schelle)
- Rise of chemical analysis and synthesis
- 1790: metric system = universal system of measurement
- Birth of agricultural chemistry (Boussingault, Mulder and Liebig)
- 1750: steam engines
- 1828: first railway line in France
- 1840: first harvester in America
First industrial revolution: the railway
~1850 – 1890

Milk
- Installation of cattle sheds in large towns to obtain fresh milk
- 1857: concentrated milk obtained by partial vacuum evaporator
- 1860: invention of Camembert box (Ridel)
- 1879: Laval centrifugal separator
- 1895: milk pasteurization (Emile Duclaux)
- Transportation of milk by rail
- 1889: sterilized milk
Science and Technology
- 1857: discovery of pasteurization (Pasteur)
- 1859: theory of evolution (Darwin)
- 1865: hybridization research (Mendel’s laws of inheritance)
- 1869: periodic table of chemical elements (Mendeleev)
- 1872: study of bacteria (Ferdinand Julius Cohn)
- 1869: invention of refrigerating machine (Charles Tellier)
- 1872: petrol engine
Second industrial revolution: petrol engine
~ 1890 – 1930
Milk
- Industrial butter factories
- Industrial pasteurization and packaging of milk
- Dry-heat and steam sterilizers
- Creation of National Dairy Industry Schools
- Industrial yoghurt manufacturing
- 1921: first French Protected Designation of Origin cheese (Roquefort)
Science and Technology
- 1900: research into yoghurt fermenting agents (Metchnikoff)
- 1910: isolation of cheese fermenting agents (Mazé)
- 1913: discovery of vitamin A
- 1918: hybrid maize
- 1927: discovery of penicillin (Fleming) and BCG
- 1892: first plastic made from milk casein
- 1895: milk pasteurization (Emile Duclos)
- 1911: domestic refrigerators
- First European automobile (André Citroën)
Third industrial revolution: automation
~ 1930 – 1980

Milk
- 1935: industrial manufacturing of cheese from pasteurized milk
- 1954: distribution of milk in French schools
- 1962: birth of the CAP in the European Union
- Generalization of milking machines and milk refrigeration on farms
- 1967: ultrafiltration
- Milk collection by isothermal tankers
- 1969: quality-based milk payments in France (Godefroy law)
Science and Technology
- Nuclear energy
- 1935-1952: start of molecular biology
- 1953: DNA structure
- 1959: first human in vitro fertilization (Edwards)
- 1962: synthetic proteins
- 1978: rise of the biotechnology industry
- 1946: first artificial insemination of cows in France
- 1960: laser beam
- 1969: first steps on the moon (Armstrong and Aldrin)
- UHT milk
- Electronic chip
Fourth industrial revolution: ICT
~ 1980 – 2000
Milk
- Industrial quality measures
- 1980: microfiltration
- 1980 to 1990: new molecular biology techniques (PCR, etc.)
- 1984: nanofiltration
- Mechanical handling of cheese
- Freeze-drying (1953) to conserve more than 3,000 strains of lactic bacteria
- 1984: dairy quotas in the European Union
- 1999: creation of the French Charter of Good Agricultural Practices
Science and Technology
- 1986: cloning of a sheep
- 1996: mapping of bovine genome in France
- 1980: implantation in France of the laser
- 1981: “TGV” French high-speed trains
- 1986: Mir space station
- Personal computers
- 1990: World Wide Web and public Internet
21st century: nomadism and nanotechnologies
~ 2000 – today
Milk
- 2000 – 2010: development of milking robots on farms
- 2000 – 2010: separation of fine milk compounds/development of ingredients (protein and fat)
- 2000 – 2010: increasingly fine analytical methods (molecular, immunological, electronic, optical, etc.)
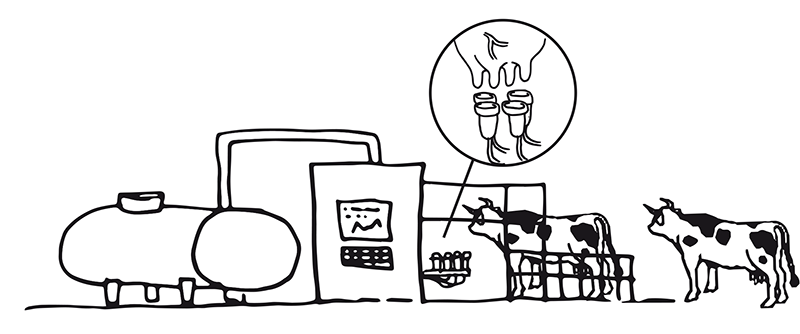
Science and Technology
- 2003: complete sequencing of the human genome
- Nanotechnologies and miniaturization
- 2006: sequencing of the bovine genome
- 2009: first official genomic indexing of bulls
- 2011: genomic indexing of cows
- 2003 – 2005: web 2.0
- 2007: rise of photovoltaics




 Everything you need to know about milk and dairy products, the different steps involved in processing them, their diversity and health benefits. Also, practical information such as how to read food labels, make homemade dairy products,…
Everything you need to know about milk and dairy products, the different steps involved in processing them, their diversity and health benefits. Also, practical information such as how to read food labels, make homemade dairy products,… All about how CNIEL serves the French dairy industry. The organization addresses a wide range of issues, from the dairy economy, international business and promotion, to technology and scientific research. Its work is aimed at helping dairy producers and processors to anticipate market developments and build a strong future.
All about how CNIEL serves the French dairy industry. The organization addresses a wide range of issues, from the dairy economy, international business and promotion, to technology and scientific research. Its work is aimed at helping dairy producers and processors to anticipate market developments and build a strong future.